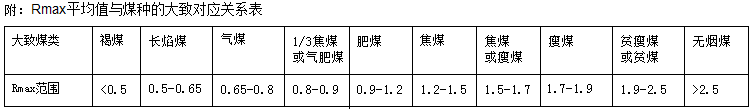
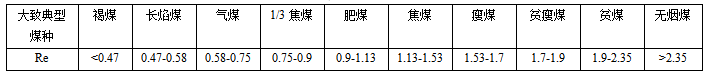
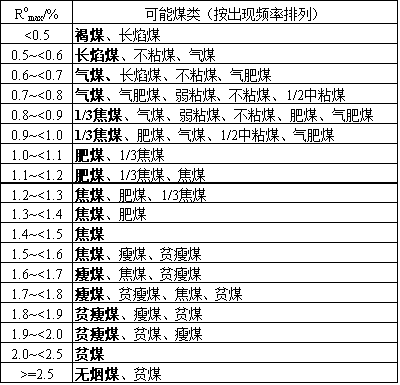
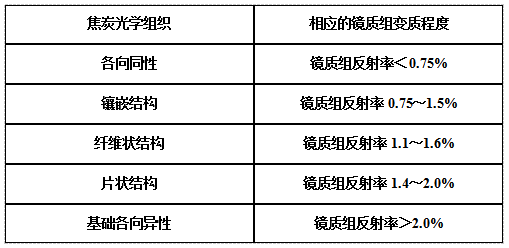
The general relationship between the vitrinite group and the coke optical structure in different degrees of metamorphism in coal
Macro analysis of coal rock types
According to the combination of macro coal and rock components and the average gloss intensity reflected by it, it can be divided into four types of macro coals, namely: bright coal, semi-light coal, semi-dark coal and dull coal.
1. Bright coal
It is the strongest layering of the luster in the coal seam.
It is mainly composed of mirror coal and bright coal (>80%), and the gloss is very strong. Because the composition is relatively uniform, it is often a uniform or inconspicuous linear structure. Endogenous fissures develop, are brittle, and are easily broken. The quality of bright coal is the best, and the best coallurgical coking coal is the degree of coalification.
2. Semi-bright coal
Bright coal and mirror coal account for the majority (50% to 80%) and contain dark coal and silk charcoal. The gloss intensity is slightly weaker than bright coal. Due to the alternating appearance of various macroscopic coal and rock components, there is often a strip-like structure. An angular or stepped fracture.
3. Semi-dark coal
The content of mirror coal and bright coal is less (50%~20%), while the content of dark coal and silk carbon is more, and the gloss is dim. It often has a strip shape, a line shape or a lenticular structure. The hardness, toughness and specific gravity of semi-dark coal are relatively large, and the quality of semi-dark coal is mostly poor.
4. Dim coal
The content of mirror coal and bright coal is very small (<20%), while it is mainly dark coal, sometimes containing more silk charcoal. The gloss is dim, not obvious, and the block structure is linear or lenticular. It is dense and hard, with high toughness and great specificity. The quality of dim briquette is mostly poor, but the dim briquette with more shells has better quality and a smaller specific gravity.
| 


















